In a certain laboratory, clean room to avoid contamination of operators and working environment by microbial aerosols.
To achieve one isolation in between the microbial biological safety cabinet must be used.
Many biological operations in the lab can produce aerosols, such as pipette operation, centrifugal precipitation, dipping liquid with inoculation ring, opening flask, mechanical vibration, strain dilution or inoculation operation, etc. In addition, some accidents during experimental operation, such as liquid pouring or splashing, can produce aerosols.
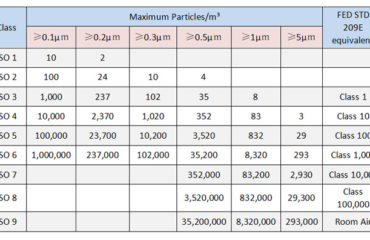
The size of the aerosol is 1-5µm which cannot be observed by the naked eye, so laboratory operators are usually not aware of the aerosol generation during operation and may be inhaled, or cause cross contamination with other experimental materials on the work table during the laboratory process.
Proper use of biological safety cabinets can effectively reduce laboratory acquired infections due to aerosol exposure and cross contamination between experimental materials. At the same time, biological safety cabinets can also play a role in protecting the environment. Therefore, biological safety cabinets are widely used in microbial laboratories.
There are 3 types of the biological safety cabinet, as below:
| Rank | Type | Exhaust | Circulate air rate (%) | Air flow Inside | Average wind speed in working window (m/s) | Protect |
| Ⅰ | Indoor exhaust | 0 | Sinuous flow | ≥0.4 | Operator & Environment | |
| Ⅱ | A1 | Indoor exhaust | 70 | Uniflow | ≥0.4 | Operator, Testing sample & Environment |
| A2 | Indoor exhaust | 70 | Uniflow | ≥0.5 | ||
| B1 | Non indoor exhaust | 30 | Uniflow | ≥0.5 | ||
| B2 | Non indoor exhaust | 0 | Uniflow | ≥0.5 | ||
| Ⅲ | Non indoor exhaust | 0 | Sinuous flow/Uniflow | No working window inlet, when one hand sleeve is removed, the wind speed of the glove mouth≥0.7 | Main for Operator & Environment, sometimes for testing sample |